-
Products
-
Bioreactor Fermenter
- Glass Bioreactor
- Parallel Bioreactor
- Stainless Steel Bioreactor
- Stainless Steel Fermenter
- Industrial Bioreactor Fermenter
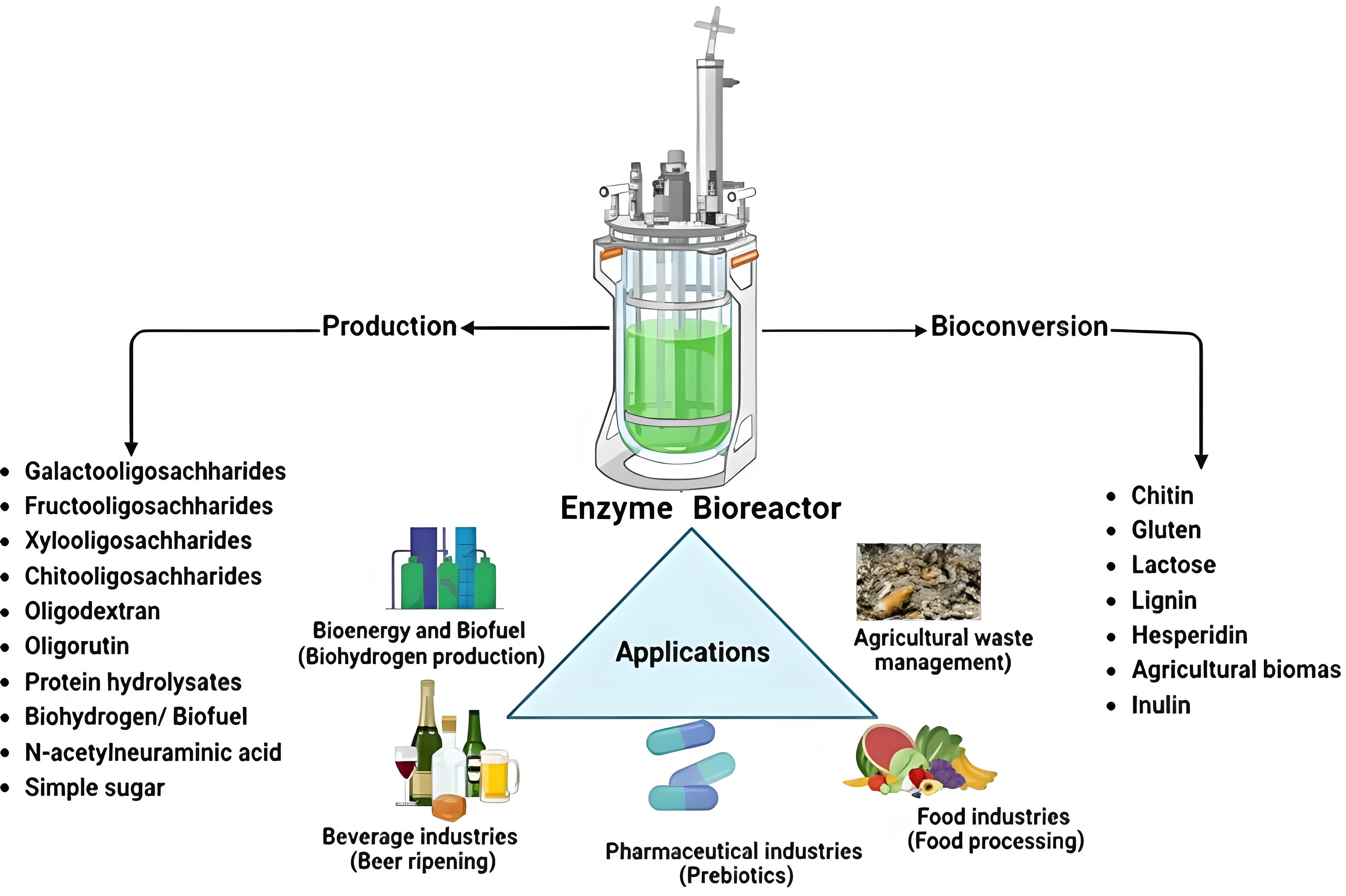
- Enzyme Bioreactor Fermenter
- Mammalian Cell Bioreactor
- Vaccine Bioreactor
- Solid State Fermenter
- Airlift Fermenter
- Photobioreactor
- Fully Automatic CIP System (Acid and Alkali)
- Industrial Process Equipment
- Centrifuge Separator
-
Suppository Production Line
- Alu Alu suppository production line
- Full Automatic Suppository Filling and Sealing Machine with 1Filling Head
- Suppository making shell machine for sale
- Sinotech 15Model Suppository Making Machine
- Suppository filling and sealing machine with 1 filling head
- Full-automatic Suppository Production Line SJ-2L
- Suppository filling machine
- Suppository Filling And Sealing Machine
- 6 Heads Suppository Forming Machine
- 7 Filling Heads Continuously Automatic Suppository Production Line
- 3 filling heads Sinotech-SL suppository filling and sealing production line
- Lab Type Semi Suppository Filling And Sealing Machine
- SJ-1LB Lab Semi Suppository Production Line
- Soft Gel Production Line
-
Tablet Press Machine
- ZP27D Rotary Salt Tablet Press Machine
- zp15/17/19 Paint style tablet press machine
- ZPS-8/10/16 Intelligent rotary tablet press
- Zp9 Rotary Tablet Press Machine
- Zp29/31/33 Multifunction Herb Tablet High Speed Double Sided Tablet Press
- Hydraulic Tablet Press
- Medical Tablet Press Machine
- Salt Tablet Press Machine
- Candy Tablet Press Machine
- Tablet Press Punch Die TDP Mold ZP Mold
- Big Size Two Layer Double Color Dishwashing Tablet Automatic Rotary Effervescent Tablet Press Machine
- Thp Series Big Flower Basket Tablet Press Machine
- ZP-31D Rotary Tablet Press
- ZP-45D Rotary Tablet Press
- ZPW-17D Rotary Tablet Press
- ZPW-23 Three Layer Press Machine
- Single Punch Tablet Press
- ZP15D 17D 19D Rotary Tablet Press
- Chicken Essence Block Production Line
-
Capsule Filling Machine
- Njp200 Pharmaceutical Automatic Softgel Hard Capsule Filling Machine
- Njp400 Model Gel Capsule Filling Machine for Herbal Powder
- NJP600 Capsule Filling Machine
- NJP800 Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- NJP1200 Fully Automatic Capsule Filling Machine
- Njp2500 Automatic Hard Gelatin Capsule Filler Machine
- NJP3800 Capsule Filling Machine
- Cgn-280-D Semi-Automatic Capsule Fill Machine
- NJP7500 Capsule Filling Machine
- CE Pharmaceutical Hard HPMC/Gelatin/Halal/Vegetarian/Hollow/ Pullulan/Empty/Hard/Vegetable/Clear Capsules Filling Packing Machine/Encapsulation Machine
- High Capacity Horizontal Capsule Polish Machine with Sorter
-
Packing Machine
- Small Automatic Chilli Powder Chili Pepper Seasoning Spice Salt Sugars Sachet Weighing Packaging Packing Machine
- Automatic Flour Chili Pack Bag Small Sachet Granule Milk Powder Filling Machine Powder Sachet Packing Machine
- Lab Type Semi Blister Sealing Machine For Capsule /Tablet/Softgel
- Lab Type Semi Blister Sealing Machine
- YD-420F Model Surprise Egg Blister Packing Machine
- DPH-260 Model High Speed Blister Packing Machine
- DPP-270S Blister packing machine (blister with paper card)
- DDP-140 Automatic Electric Blister Packing Machine for Tablet Pills Capsule
- Tablets Automatic Alu-pvc Blister Packing Machine
- DPP 80 Automatic Jam Honey Blister Packaging Machine with Peristaltic Pump
- DPP-80 Automatic Aluminum Plastic Blister Packing Machine Capsule Blister Packing Machine
- Full Automatic Oil Liquid Blister Packaging Honey Chocolate Sauce Cream Syrup Food Jelly Blister Packing Machine
- Fully Automatic Butter Cheese Paste Cream Blister Packing Machine
- Desktop Blister Sealing Machine
-
Tablet Counting Machine
- Automatic 16 Channel Vibration Intelligent Visual Capsule Counting Machine
- High Efficient Tablet Pharmaceutical Production Line
- Pharmaceutical Grade Tablet Pill Counting Machine
- Multi Channel Automatic Vibrating Bottle Capsule Counting Machine
- Automatic Candy Bottle Counting Machine
- Benchtop Tablets Capsules Pills Counting Machine
- YL-8 Lane Electric Automatic Softgel Capsule Tablet Counter 8 Channel Bottling Capsule Tablet Counting Machine
- Yl-2A Desktop Small Electronic Tablet Counter
- YL-2 Tablet Capsule Candy Softgel Counting Machine
- Freeze Dryer
- Spray Dryer
- Membrane Filtration Equipment
-
Filling Machine
- ST-100R Automatic High Speed Coffee Capsule Filling and Sealing Machine
- ST-KJ400 Automatic High Speed Coffee Capsule Filling and Sealing Machine
- 240 Model Oral Liquid Plastic Ampoule Filling Sealing Machine
- Oral Liquid Plastic Ampoule Filling Sealing Machine
- SINOTECH250-B Automatic Tube Filling and Sealing Machine
- SINOTECH350-B Model Automatic Plastic Tube Filling and Sealing Machine
- Fully Automatic Filling Sealing Machine for Plastic Toothpaste Tube Soft Cosmetic Cream
- Single filling head YD300A--automatic Cartridge filling machine
- 200L Hydraulic Extruder --(SINOTECH)
- Coffee Capsule Filling and Sealing Machine
- High Speed Linear Type Coffee Capsule Filling and Sealing Machine
- DJ-50D multifunctional vertical box filling machine
- SINOTECH-60S Automatic Aluminum tube filling and Sealing Machine
-
Bioreactor Fermenter
- Project
- Company
- Application
-
Services
- Blog
- Resources
- Contact
 English
English français
français Español
Español русский
русский português
português العربية
العربية Deutsch
Deutsch tiếng việt
tiếng việt 한국어
한국어 Türkçe
Türkçe Malay
Malay